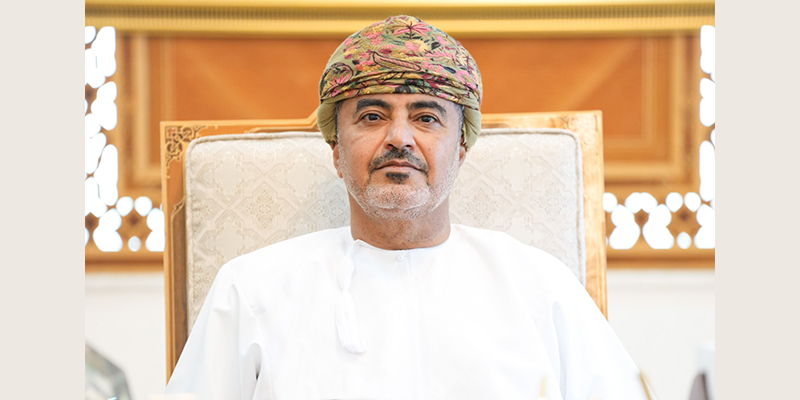
03 Apr Interview with H.E. Eng. Said bin Hamood bin Said Al Mawali, Minister of Transport, Communications and Information Technology, Oman
JT: How is the Ministry aligning its strategies to drive Oman Vision 2040, and what key initiatives are currently underway to promote economic diversification?
Al Mawali: The Ministry of Transport, Communications, and Information Technology (MTCIT) is central to Oman Vision 2040, driving digital transformation, infrastructure development, and economic diversification. A key focus is modernizing Oman’s ports—Salalah, Duqm, Sohar, and Khasab—to strengthen the country’s position as a global logistics hub. Smart logistics, automation, and digital customs systems are improving efficiency, while investments in road networks and planned railway connections enhance trade and connectivity. Beyond infrastructure, Oman is advancing its digital economy, aiming to raise its GDP contribution from 2% to 10%. The National Program for Digital Economy integrates AI, big data, and fintech, supported by initiatives in e-commerce, cybersecurity, and space technologies. Public-private partnerships are fostering investment in data centers and emerging tech industries, reinforcing Oman’s position as a regional digital leader. To support this transformation, the Ministry is equipping Omanis with future-ready skills through programs like Makeen, training 10,000 youth in AI, cybersecurity, and cloud computing. Sustainability is also a priority, with efforts to reduce carbon footprints and integrate green technologies. By enhancing trade, fostering innovation, and creating a skilled workforce, Oman is positioning itself as a dynamic and competitive business destination.
JT: What strategies is the Ministry implementing to enhance telecommunications infrastructure and digital communication networks in Oman, and how will these improvements benefit businesses and citizens?
Al Mawali: ICT is a cornerstone of Oman’s transformation, with the Ministry leading efforts to enhance telecommunications infrastructure and digital services. By mid-2024, Oman had 5,431 operational 5G stations, with 99% of telecom sites supporting both 4G and 5G. Fiber-optic coverage has expanded to 61% of residential units, with over 101,000 new connections completed this year. The country’s position as a regional digital hub is reinforced by 21 submarine internet cables, ensuring global connectivity. Oman’s telecom sector continues to grow, with 10 licensed providers and six data centers supporting the rising demand for cloud services. Mobile broadband penetration has reached 98%, and 67% of priority government services have been digitalized, with plans to reach 80% by 2025. Government digital transactions surged to 27 million in 2024, up from 9.5 million in 2023. These advancements are reflected in Oman’s improved global rankings: it climbed nine places to 41st in the E-Government Development Index, five places to 45th in AI readiness, and four places to 50th in the Network Readiness Index. Oman also holds a Tier 1 ranking in cybersecurity, placing 21st globally.
JT: What steps is the Ministry taking to incorporate sustainability into Oman’s new transport infrastructure?
Al Mawali: Sustainability is central to Oman’s transport strategy, aligned with Vision 2040 and the goal of net-zero emissions by 2050. The Ministry is promoting electric and hydrogen-powered transport, expanding electric vehicles (EV) charging stations, and integrating clean energy into infrastructure. Roads are becoming more sustainable with rubber-modified asphalt and micro-surfacing technology to enhance durability. In public transport, dedicated bus lanes in Muscat encourage ridership and reduce emissions. Ports are also transitioning to electrified equipment and renewable energy, while pilot projects explore hydrogen-powered heavy transport and marine vessels in collaboration with industry and research partners. These initiatives position Oman’s transport network for a greener future.
JT: How does the Ministry plan to leverage these technologies to enhance the efficiency and safety of Oman’s transport and communication systems?
Al Mawali: Oman is embracing AI, blockchain, and IoT to enhance transport efficiency, safety, and sustainability. AI-powered traffic management systems optimize road flow and predictive maintenance, while blockchain is streamlining trade and logistics, successfully tested at Sohar Port. IoT-based smart sensors improve road safety and infrastructure monitoring, and digital public transport services, including smart ticketing and real-time tracking, are enhancing urban mobility. The Ministry is also launching an Open Data Platform, providing real-time transport and communication data to support AI analytics and blockchain-secured transactions. These innovations ensure Oman’s transport system remains resilient, future-ready, and globally competitive.
JT: How is the Ministry strengthening Oman’s role as a logistics and trade hub on the global stage?
Al Mawali: Oman is strengthening its position as a global logistics and trade hub by leveraging its strategic location and investing in key infrastructure. The Ministry is expanding port and airport capacities, improving connectivity between free zones and logistics corridors, and integrating these hubs into global trade networks. Digitization is also a priority, with automated customs systems and the Port Community System (PCS) reducing cargo clearance times by up to 46%. Additionally, public-private partnerships (PPPs) are attracting global logistics companies to invest in Oman’s supply chain infrastructure. International collaboration plays a crucial role, with Oman securing MOUs with GCC nations, global maritime operators, and transport technology firms. These partnerships support infrastructure modernization, enhance regional and global connectivity, and position Oman as a critical transit hub linking Asia, Africa, and Europe.
JT: What opportunities do you foresee for collaboration between Oman and Japan in the development of the Muscat metro?
Al Mawali: The Muscat Metro project, poised to transform Oman’s urban mobility landscape, presents an exciting opportunity for collaboration, particularly with Japan, which has a long-standing reputation for developing world-class metro systems. The partnership could bring in Japanese expertise in automation, smart metro solutions, and energy-efficient design, all of which could contribute to a sustainable and efficient metro system. With Japan’s experience in developing green metro infrastructure, the project could significantly reduce its environmental impact. Further collaboration could include public-private investments, allowing both Omani and Japanese firms to jointly work on the construction, operation, and long-term maintenance of the metro system. Japan’s advanced rail systems, known for their precision scheduling and automated control, could enhance the operational efficiency and safety of the Muscat Metro, making it a model of urban mobility.
JT: Do you have any closing remarks for our readers who are considering visiting or investing in Oman?
Al Mawali: Oman is emerging as a prime destination for both investment and tourism, thanks to its strategic location, world-class infrastructure, and investor-friendly policies. With easy access to the GCC, Africa, and the Indian subcontinent, Oman is a key trade hub, benefiting from global shipping routes and strong diplomatic relations. The country offers stable economic conditions, a competitive logistics ecosystem, and attractive incentives for investors, including tax exemptions and access to major infrastructure projects through Invest Oman. Oman’s focus on innovation and sustainability further enhances its appeal as a long-term investment destination. For visitors, Oman’s rich culture, natural beauty, and modern connectivity make it an ideal place to explore. Whether for business or leisure, Oman offers exceptional opportunities for growth and discovery.